The team of Shenzhen Lingpao Technology Co., Ltd. was established in 2021, focusing on data communication industry, Internet of Things, security monitoring and other intelligent hardware, providing high-quality products and solutions. The company’s headquarters is located in Nanshan High-tech Industrial Park , Shenzhen, has a complete independent research and development, manufacturing, and sales system.
Mantener estrechos intercambios técnicos y cooperación con Qualcomm, Realtek, MTK, Intel y otros conocidos fabricantes de chips del sector, y mejorar continuamente el nivel técnico y la capacidad de servicio.
The factory covers an area of 5000+square meters, has 10 SMT high-speed lines, and has ISO9001 quality certification system. The product is exported to more than 10 countries and regions.
The existing products cover wireless, routers, switches, security monitoring, industrial equipment, integrated wiring and other fields, with strong R & D, manufacturing, marketing capabilities for global operators, integrators and end users to provide “high quality, high stability, cost-effective” products and services.
FAQ Guide
Let’s continue!
1.What is a PoE++ Switch?
2.What is a PoE+ Switch?
3.What is a PoE Switch?
4.How does a POE switch prioritize power delivery?
5.What are the safety features of a POE switch?
6.Can a POE switch be used for outdoor installations?
7.What is the range of a POE switch’s power delivery?
8.What is the difference between a managed and unmanaged POE switch?
9.Can a POE switch be used for both data and power transfer?
10.Are there any compatibility issues with POE switches and devices?
11.What is the process for adding or removing devices from a POE switch?
12.Does a POE switch require any additional equipment or setup?
13.Can a POE switch be used in a network with non-POE devices?
14.What type of cable is required for a POE switch?
15.Can multiple POE switches be connected together?
16.What is the warranty for a POE switch?
17.Are there any special configurations or settings needed for a POE switch to function properly?
18.How to choose between POE, POE+ and POE++
1.What is a PoE++ Switch?
A PoE++ switch is a type of network switch that supports the latest and most powerful Power over Ethernet (PoE) standard, known as PoE++. This standard is defined by the IEEE 802.3bt specification. There are two types of PoE++ switches: Type 3 and Type 4.
PoE++ switches are ideal for scenarios such as deploying advanced surveillance systems, high-performance wireless networks, and industrial automation systems.
Key POE++ (802.3bt) specifications:
Power Delivery (Type 3): Up to 60 watts per port.
Power Delivery (Type 4): Up to 100 watts per port.
Voltage: 50-57 volts DC.
Current (Type 3): Up to 960 mA.
Current (Type 4): Up to 1,400 mA.
Total Power Budget: Depends on switch and configuration.
Notable Applications: High-performance access points, PTZ cameras, advanced IoT devices.
2.What is a PoE+ Switch?
A PoE+ switch (commonly called a PoE, Type 2 switch) is a type of network switch configured to support the IEEE802.3at standard. POE+ offers higher power delivery compared to the original POE (802.3af) standard.
Key PoE+ (802.3at) Specifications:
Power Delivery: Up to 30 watts per port.
Voltage: 50-57 volts DC.
Current: Up to 600 mA.
Total Power Budget: Typically 25.5 watts (after power loss considerations).
Notable Applications: Wireless access points, advanced IP cameras, some VoIP phones.
3.What is a PoE Switch?
A Power over Ethernet (PoE) switch (commonly called a PoE, Type 1) is a network switch that is equipped with the capability to deliver both data and electrical power over Ethernet cables to connected devices. This eliminates the need for separate power cables and power sources for those devices, simplifying installations and reducing cable clutter.
RCS7150-12M has power over ethernet (PoE) on all 12 ports
Pictured here, the RCS7150-12M has power over ethernet (PoE) on all 12 ports. All the ports are at least 15.4W, and four are 30W capable, for maximum power throughout the switch.
Key PoE (802.3af) Specifications:
Power Delivery: Up to 15.4 watts per port.
Voltage: 44-57 volts DC.
Current: Up to 350 mA.
Total Power Budget: Typically 12.95 watts (after power loss considerations).
Notable Applications: Phones, basic cameras, access points, switches, accessory edge devices.

4.How does a POE switch prioritize power delivery?
Power over Ethernet (POE) switches use a technique called power prioritization to manage the power delivery to connected devices. This involves several steps:
Detection: The POE switch first detects whether the connected device is a POE-enabled device. This is done through a process called power classification, where the switch sends a low-voltage signal to the device and receives a response indicating its power requirements.
Negotiation: If the device is POE-enabled, the switch and device negotiate the amount of power that can be delivered. This negotiation is based on the power class of the device and the available power on the switch.
Allocation: Once the negotiation is complete, the switch allocates the required amount of power to the connected device.
Power budgeting: POE switches have a limited power budget, so they need to manage the power delivery to multiple devices. They do this by keeping track of the amount of power allocated to each device and making sure it does not exceed the total power budget.
Priority assignment: In cases where there are multiple devices connected to the POE switch, it needs to prioritize which devices will receive power in case of a power shortage. This is where power prioritization comes into play.
POE switches use various methods for power prioritization, including first-come-first-served, round-robin, and weighted round-robin. These methods prioritize devices based on their power requirements, usage, and criticality. For example, a device that is essential for network operations may be given a higher priority than a less critical device.
5.What are the safety features of a POE switch?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Output Protection: This feature ensures that the power being supplied through the Ethernet cables is within safe limits, preventing any damage to connected devices.
Short Circuit Protection: POE switches have built-in protection against short circuits, ensuring that the switch and connected devices are not damaged in case of a short circuit.
Temperature Control: POE switches have sensors that monitor the temperature and automatically adjust the power supply to maintain safe operating levels.
Surge Protection: POE switches have built-in surge protection to shield connected devices from sudden power surges or spikes, preventing any potential damage.
Intelligent Circuit Design: The circuit design of POE switches is optimized to minimize the risk of electrical faults, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
Power Monitoring: POE switches have the ability to monitor the power usage of connected devices, allowing network administrators to identify potential safety issues and take corrective actions.
VLAN Support: Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) functionality in POE switches allows network administrators to segment the network, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive areas.
6.Can a POE switch be used for outdoor installations?
Yes, a POE (Power Over Ethernet) switch can be used for outdoor installations. However, the switch must be specifically designed for outdoor use, as regular indoor switches are not equipped to handle harsh outdoor conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, and dust.
Outdoor POE switches are typically made with a ruggedized casing and are weatherproof to protect against the elements. They also have a higher level of surge protection to prevent damage from power surges or lightning strikes.
In addition, outdoor POE switches must also have the proper IP (Ingress Protection) rating to ensure they are suitable for the specific outdoor environment where they will be installed. IP ratings indicate the level of protection against solid objects (first digit) and liquids (second digit), with a higher rating indicating better protection. For example, an IP65 rating means the switch is completely protected against dust and can withstand low-pressure water jets from any direction.
Overall, using a POE switch for outdoor installations can be a cost-effective and efficient solution for connecting and powering outdoor devices such as security cameras, Wi-Fi access points, and outdoor lighting. However, it is important to ensure that the switch is specifically designed and rated for outdoor use to ensure reliable and safe operation.
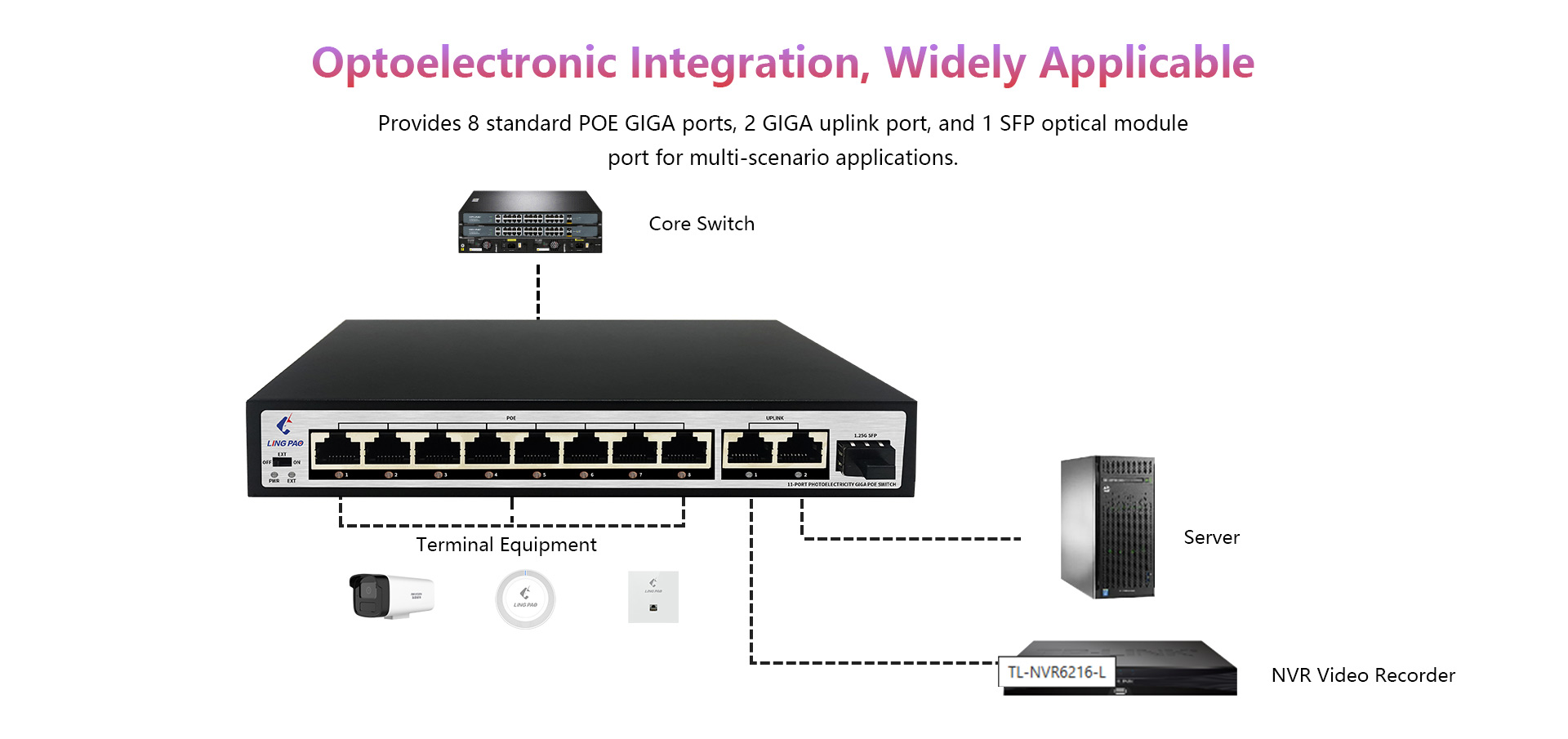
7.What is the range of a POE switch’s power delivery?
The range of a POE switch’s power delivery can vary depending on the specific model and capabilities of the switch. However, most POE switches are designed to deliver power within a range of 15.4 to 30 watts per port. This means that the switch can provide up to 15.4 watts of power to each connected device, and the total power output of the switch may vary depending on the number of ports and the overall power budget of the device. Some high-end POE switches may also offer extended power delivery capabilities of up to 60 watts or more per port. Additionally, the length of the Ethernet cable used to connect the device may also affect the power delivery range, with longer cables resulting in a decrease in power delivery. It is important to check the specifications of a particular POE switch to determine its specific power delivery range.
8.What is the difference between a managed and unmanaged POE switch?
A managed POE (Power over Ethernet) switch refers to a type of network switch that can be configured and controlled by network administrators. It allows for advanced features such as Quality of Service (QoS) settings, VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks), and traffic prioritization.
On the other hand, an unmanaged POE switch is a plug-and-play device that does not offer any advanced configuration options. It is designed for basic networking needs and does not require any technical knowledge to set up. Unmanaged switches are typically used in smaller networks with simpler needs.
the main difference between a managed and unmanaged POE switch is the level of control and customization options available for network administrators. Managed switches offer more advanced features and can be tailored to specific network requirements, while unmanaged switches are simpler and easier to use for basic networking needs.
9.Can a POE switch be used for both data and power transfer?
Yes, a POE (Power over Ethernet) switch is designed to provide both data and power transfer capabilities. It can support both regular Ethernet data connections, as well as transmit power over the same Ethernet cable to PoE-enabled devices such as IP phones, wireless access points, and security cameras. This makes POE switches a convenient and cost-effective solution for powering devices in areas where traditional power outlets may not be easily accessible, such as in ceilings or on poles. Additionally, POE switches typically have advanced management features that allow for efficient power management and monitoring of PoE devices.

10.Are there any compatibility issues with POE switches and devices?
Yes, there can be compatibility issues between POE switches and devices. Some potential issues include:
- Power requirements: POE switches have a limited power supply, and some devices may require more power than the switch can provide. This can lead to the device not receiving enough power and not functioning properly.
- PoE standards: There are different standards for POE, with the most common being IEEE 802.3af and 802.3at. If a switch and device are not using the same standard, they may not be compatible.
- Incompatibility with non-POE devices: Some POE switches may not be compatible with non-POE devices, as they are designed specifically for powering POE-enabled devices.
- Cabling issues: POE switches require a certain type of cabling, such as Cat5e or Cat6 in order to provide power. If the cabling is not compatible, the switch and device may not work together.
To avoid compatibility issues, it is important to make sure that both the switch and devices are POE-enabled and using the same standard. It is also recommended to use compatible cabling to ensure proper power supply.
11.What is the process for adding or removing devices from a POE switch?
The process for adding or removing devices from a POE switch involves the following steps:
- Power off the POE switch: Before adding or removing any devices, ensure that the POE switch is powered off to avoid any accidents or damage.
- Identify the specific port: Identify the port on the POE switch where you want to add or remove the device.
- Connect the device: If you want to add a device, connect it to the designated port on the POE switch. Make sure the connection is secure and the device is functioning properly.
- Check for power requirements: If the device is a POE device, then it will receive power directly from the switch. If it is a normal device, you may need to use a POE injector to supply power to the device.
- Configure the new device: Once the device is connected, you may need to configure its settings to ensure it works properly with the POE switch. This may include setting up network settings or assigning a static IP address.
- Test the connection: After configuring the new device, test the connection to make sure it is functioning properly and is able to communicate with other devices on the network.
- Update documentation: Once the device is successfully added, update any network documentation to reflect the new device and its location on the POE switch.
- For removing a device, simply disconnect it from the designated port on the POE switch and update network documentation accordingly.
- Power on the POE switch: After adding or removing devices, power on the POE switch and ensure all devices are functioning correctly.
It is important to follow these steps carefully to avoid any network disruptions or damage to the devices or the POE switch.
12.Does a POE switch require any additional equipment or setup?
Yes, a POE (Power over Ethernet) switch may require additional equipment and setup depending on the specific needs and requirements of the network.
Firstly, the POE switch will require POE-enabled devices such as IP cameras, wireless access points, or VOIP phones that are capable of receiving data and power through the same network cable. If the network devices are not POE-enabled, then additional POE injectors or splitters may be needed to power them.
Additionally, the POE switch may require a power source, which can be either a standard AC power adapter or a backup battery in case of a power outage. In some cases, an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) may also be required to ensure uninterrupted power supply to the POE switch, especially in critical network environments.
Furthermore, proper network setup and configuration are essential for the POE switch to function correctly. This may involve configuring the switch with the appropriate settings, assigning network addresses, and managing the POE power budget to ensure the switch can provide sufficient power to all connected devices.
while a POE switch offers the convenience of powering devices through the same network cable, it may require additional equipment and setup to properly function in a network environment. It is essential to carefully consider the power needs and network requirements before implementing a POE switch in a network.

13.Can a POE switch be used in a network with non-POE devices?
Yes, a POE switch can be used in a network with non-POE devices. POE switches have the ability to detect whether a connected device is a POE device or not. Non-POE devices will simply not receive power from the POE switch, while POE devices will receive both data and power from the switch. This allows for a mix of POE and non-POE devices to be used in the same network without any compatibility issues. Additionally, POE switches often have a mix of POE and non-POE ports, so non-POE devices can simply be connected to the non-POE ports. So, overall POE switches can be effectively used in a network with non-POE devices.
14.What type of cable is required for a POE switch?
A POE (Power over Ethernet) switch requires Ethernet cables for data transmission and power delivery. The cables used for POE switches are generally Cat5e or Cat6 Ethernet cables, which can support both data and power transfer. These cables have four pairs of wires, with two used for data transmission and the other two for power delivery. The required length and specification of the cable may vary depending on the specific POE switch and network setup. It is also important to ensure that the cable is properly shielded and meets industry standards to avoid any interference or damage to the power and data signals.
15.Can multiple POE switches be connected together?
Yes, multiple POE switches can be connected together to create a larger network. This is known as a switch stack or a cascading setup. In a switch stack, connecting cables are used to connect the switches together, forming a single logical unit. This allows for increased scalability, fault tolerance, and enhanced management capabilities such as single-point configuration and monitoring. Switches can also be connected in a cascading setup, where one switch is connected to another switch and so on, creating a network that extends beyond the capacity of a single switch. However, it is important to consider the network’s overall design and needs when connecting multiple POE switches together, as there may be limitations on power supply, bandwidth, and compatibility between different switch models.
16.What is the warranty for a POE switch?
The warranty for a POE (Power over Ethernet) switch can vary depending on the manufacturer and model of the switch. In general, most POE switches have a warranty period of 1 to 3 years. This means that the manufacturer will cover any defects or malfunctions that occur within this time frame. However, it’s important to note that the warranty does not cover damage due to misuse or accidents. Additionally, some manufacturers may offer extended warranty options for an additional cost. It’s always recommended to check the specific warranty information provided by the manufacturer for your particular POE switch.

17.Are there any special configurations or settings needed for a POE switch to function properly?
Yes, there are certain configurations and settings that may be required for a POE switch to function properly. Some of the key elements to consider are:
Power budget: It is important to ensure that the POE switch has enough power budget to support all connected POE devices. This can be determined by calculating the power requirements of each device and making sure it falls within the switch’s specified power budget.
Prioritization settings: If the POE switch has the capability to prioritize power delivery to certain devices, it is important to configure this properly. Devices that require a higher priority, such as security cameras, should be given more power than devices with a lower priority, such as IP phones.
VLAN configuration: VLANs (Virtual LANs) can be used to separate and manage different types of POE devices on the network. For example, IP phones and security cameras can be placed on separate VLANs to ensure that they receive the correct amount of bandwidth and power.
Quality of Service (QoS) settings: QoS settings can be used to prioritize certain types of network traffic, such as voice or video, over others. This can help improve the overall performance and reliability of POE devices on the network.
18.How to choose between POE, POE+ and POE++
Choosing between POE, POE+, and POE++ depends on the specific power requirements of your network devices and the capabilities of your network infrastructure. Here are some steps to help you make an informed decision:
Determine Power Needs: Assess the power requirements of the devices you intend to power over Ethernet. Different devices have varying power consumption levels. Make a list of devices and their corresponding power needs in watts.
Check Device Compatibility: Verify whether your devices are compatible with POE, POE+, or POE++. Some devices might only support specific POE standards. Check the manufacturer’s specifications or documentation to confirm compatibility.
Consider Future Growth: Think about potential future additions or upgrades to your network. If you expect to integrate higher-powered devices down the line, it might be wise to invest in a higher POE standard now to accommodate those needs.
Assess Network Switch Capability: Check if your network switch supports the POE standard you’re considering. Not all switches support all POE standards. Make sure the switch can deliver the required power levels to the devices you plan to connect.
Evaluate Cable Length and Voltage Drop: Keep in mind that longer Ethernet cable runs can lead to voltage drop and power loss. Higher-powered devices may require higher voltage levels to compensate for this drop. Consider the cable length between the switch and the powered devices.
Budget Considerations: POE++ equipment might be more expensive than POE or POE+ alternatives. Evaluate your budget constraints and balance them with the power needs of your devices.
Plan for Redundancy and Failover: If power continuity is critical for your network devices, consider redundant power sources or uninterruptible power supply (UPS) solutions. This may influence your choice of POE standard.
Consult with Professionals: If you’re unsure about which POE standard to choose, consult with IT professionals, network engineers, or vendors who specialize in networking equipment. They can provide valuable insights based on your specific use case.
Review Standards Evolution: Keep in mind that technology evolves. While POE++ might provide more power, future standards could potentially offer even higher power capacities. Consider the longevity of your infrastructure when making a decision.
In general, if you’re planning to power devices with higher power requirements or anticipate future expansion of your network, choosing a higher POE standard (such as POE+ or POE++) might be beneficial. However, always make sure to verify compatibility, assess the capabilities of your existing infrastructure, and consider your specific needs before making a decision.
